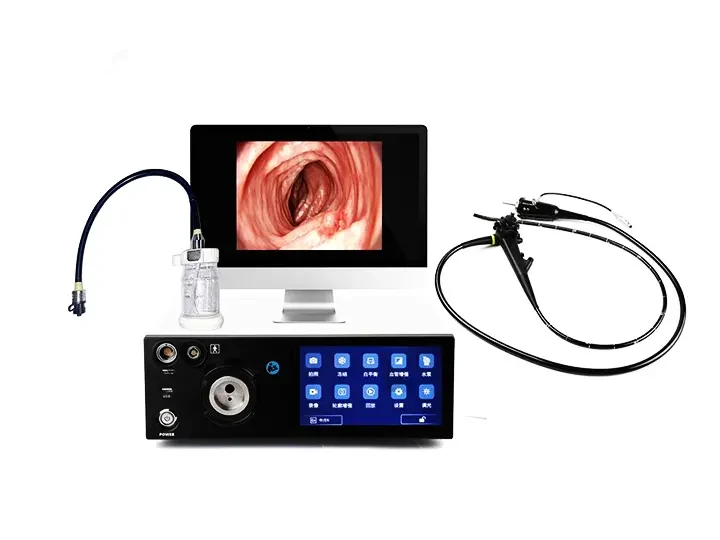
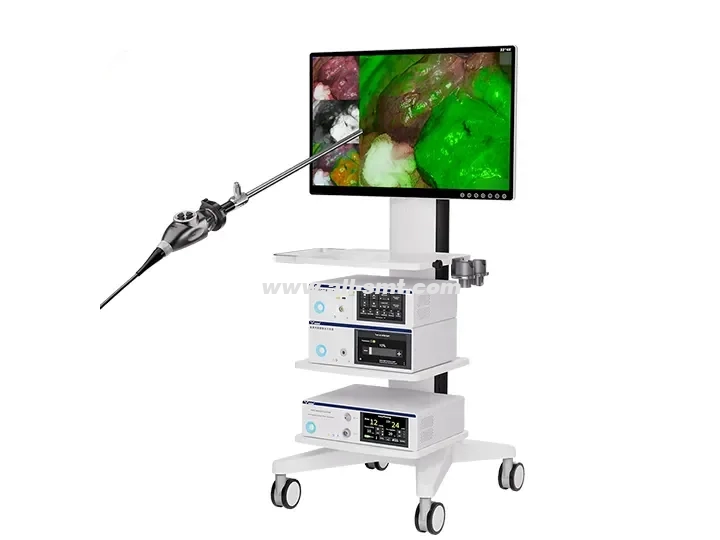
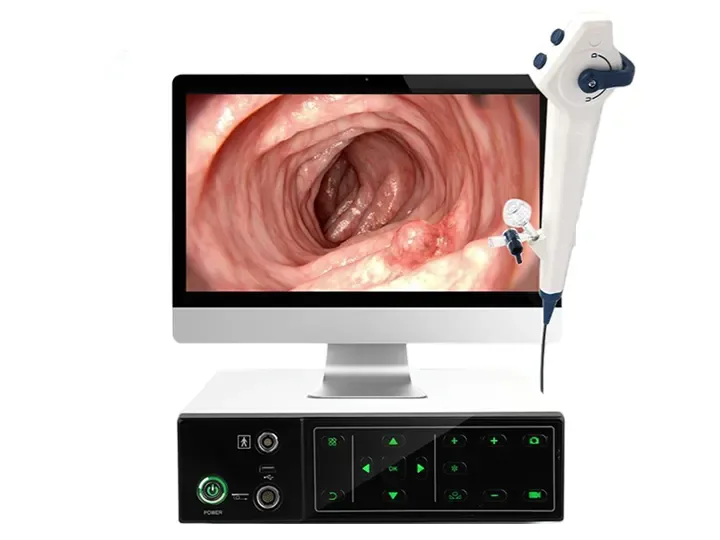
A medical endoscope is a medical device that uses optical imaging technology to observe the internal tissues or cavities of the human body. Its core principle is to achieve visual diagnosis or surgical operations through light transmission, image acquisition and processing. The following is its basic working principle:
1. Optical imaging system
(1) Illumination system
Cold light source illumination: LED or xenon lamp is used to provide high-brightness, low-heat illumination, and light is transmitted to the front end of the endoscope through the optical fiber bundle to illuminate the inspection area.
Special light mode: Some endoscopes support fluorescence (such as ICG), narrow-band light (NBI), etc. to enhance the contrast of blood vessels or diseased tissues.
(2) Image acquisition
Traditional optical endoscope (hard endoscope): The image is transmitted through the lens group, and the eyepiece end is directly observed by the doctor or connected to the camera.
Electronic endoscope (soft endoscope): The front end integrates a high-definition CMOS/CCD sensor, directly collects images and converts them into electrical signals, which are transmitted to the host for processing.
2. Image transmission and processing
Signal transmission:
Electronic endoscopes transmit image data via cables or wirelessly.
Some 4K/3D endoscopes use optical fiber or low-latency digital signals (such as HDMI/SDI) to ensure real-time performance.
Image processing: The host performs noise reduction, sharpening, and HDR enhancement on the original signal to output high-definition images.
3. Display and recording
4K/3D display: presents ultra-high-definition surgical field of view, and some systems support split screen (such as white light + fluorescence contrast).
Image storage: supports recording 4K video or screenshots for medical record archiving, teaching or remote consultation.
4. Auxiliary functions (high-end models)
AI-assisted diagnosis: real-time marking of lesions (such as polyps and tumors).
Robot control: Some endoscopes integrate robotic arms to achieve precise operation.
Summary
The core principle of medical endoscopes is:
Illumination (optical fiber/LED) → image acquisition (lens/sensor) → signal processing (noise reduction/HDR) → display (4K/3D), combined with intelligent technology to improve the accuracy of diagnosis and treatment.