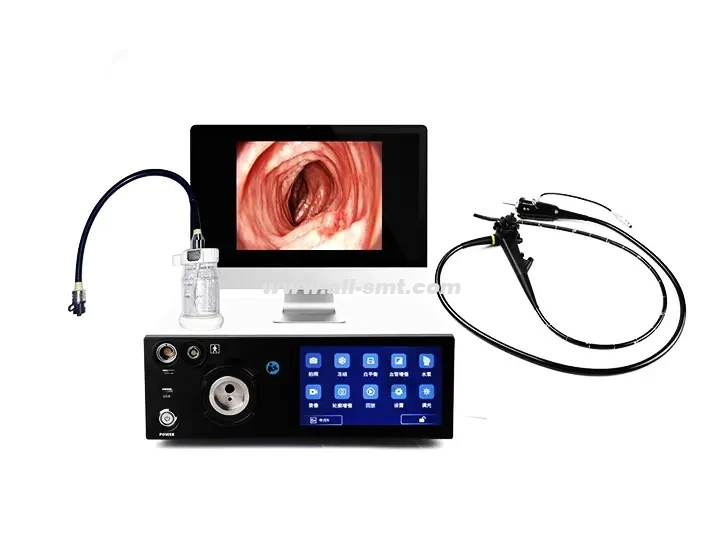
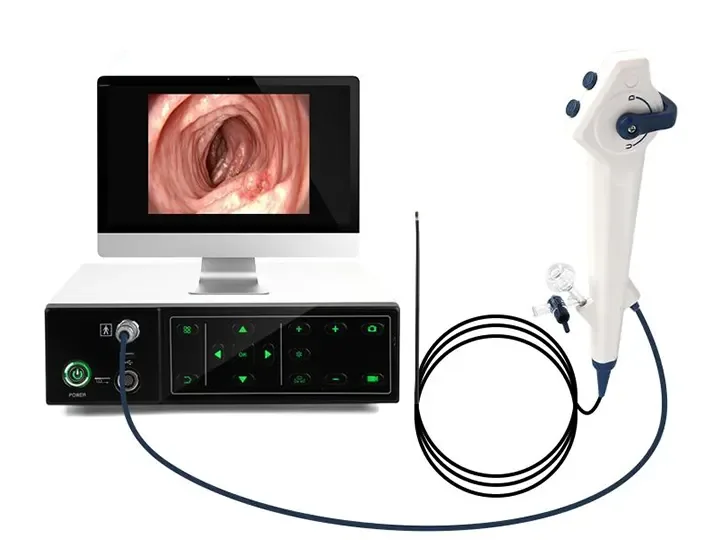
Medical gastrointestinal endoscopy equipment is a core diagnostic and treatment tool for gastroenterology and endoscopy centers. It is mainly used for the examination and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases such as gastroscopy, colonoscopy, ERCP, etc. Its core features are high-definition imaging, precise operation, safety and reliability, and the combination of intelligent technology to improve the efficiency of diagnosis and treatment. The following are its main features:
1. High-definition imaging system
(1) High-resolution imaging
4K/8K ultra-high definition: Provides 3840×2160 or higher resolution to clearly display the microstructure of the mucosa (such as capillaries and glandular duct openings).
Electronic staining technology (such as NBI/FICE/BLI): Enhances lesion contrast through narrow-band spectrum and improves the detection rate of early gastric cancer and intestinal cancer.
(2) Intelligent image optimization
HDR (high dynamic range): Balances light and dark areas to avoid reflection or loss of details in dark areas.
AI real-time assistance: Automatically marks suspicious lesions (such as polyps and tumors), and some systems can predict pathological grading.
2. Flexible operating system
(1) Scope design
Soft electronic endoscope: bendable scope (8-12mm in diameter) for easy passage through curved parts of the digestive tract.
Dual-channel therapeutic endoscope: supports simultaneous insertion of instruments (such as biopsy forceps, electrosurgical unit) to improve surgical efficiency.
(2) Precision control
Electric bending control: Some high-end endoscopes support electric adjustment of the lens angle (≥180° up, down, left, and right).
High torque transmission: reduces the risk of the scope "knotting" in the intestinal cavity and improves the success rate of insertion.
3. Multifunctional treatment capabilities
(1) Minimally invasive surgery support
High-frequency electrosurgical resection/electrocoagulation: connect electrosurgical equipment (such as ERBE) to perform polypectomy (EMR) and mucosal dissection (ESD).
Hemostasis function: supports argon gas knife (APC), hemostatic clips, injection hemostasis, etc.
(2) Expanded diagnosis and treatment mode
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS): combined with ultrasound probe, evaluates the digestive tract wall layer and surrounding organs (such as pancreas and bile duct).
Confocal laser endoscope (pCLE): achieves real-time imaging at the cellular level for early diagnosis of cancer.
4. Safety and comfort design
(1) Infection control
Removable waterproof design: the mirror body supports immersion disinfection or automatic cleaning and disinfection machine (such as Olympus OER-A).
Disposable accessories: such as biopsy valves and suction tubes to avoid cross infection.
(2) Patient comfort optimization
Ultra-fine endoscope: diameter <6mm (such as transnasal gastroscope), reducing vomiting reflex.
CO₂ insufflation system: replaces air insufflation to reduce postoperative abdominal distension.
5. Intelligence and data management
AI-assisted diagnosis: automatically analyzes lesion characteristics (such as Paris classification and Sano classification).
Cloud storage and remote consultation: supports DICOM standard and connects to hospital PACS system.
Surgery video and teaching: 4K video recording for case review or training.
Summary
The core features of medical gastrointestinal endoscopy equipment are high definition, precision, safety, and intelligence, which not only meet diagnostic needs (early cancer screening) but also support complex treatments (such as ESD and ERCP). In the future, it will further develop towards AI, minimally invasive, and convenient, improving diagnosis and treatment efficiency and patient experience.