A CO2 laser, or carbon dioxide laser, is a type of gas laser that emits infrared light at a wavelength of 10.6 micrometers. Renowned for its high efficiency and power, the CO2 laser is extensively used in various industries, including manufacturing, medicine, and research. Its ability to cut, engrave, and vaporize materials with precision makes it an invaluable tool in modern technology.

Understanding CO₂ Laser Technology
To appreciate the versatility of CO₂ lasers, it's essential to understand their underlying technology, components, and operational principles.
How CO₂ Lasers Work
CO₂ lasers operate by electrically stimulating a gas mixture composed primarily of carbon dioxide (CO₂), nitrogen (N₂), and helium (He). When an electric current passes through this mixture, it excites the gas molecules, causing them to emit infrared light. This light is then amplified within the laser cavity, producing a coherent and powerful laser beam.
Gas Mixture Composition
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): The primary lasing medium responsible for light amplification.
Nitrogen (N₂): Assists in energy transfer to CO₂ molecules.
Helium (He): Helps dissipate heat and stabilize the laser operation.
Key Components of a CO₂ Laser
A typical CO₂ laser system comprises several critical components that work in unison to generate and control the laser beam.
Laser Tube
The laser tube contains the gas mixture and is the site where the lasing action occurs. It is usually made of glass or metal and is sealed to maintain the integrity of the gas mixture.
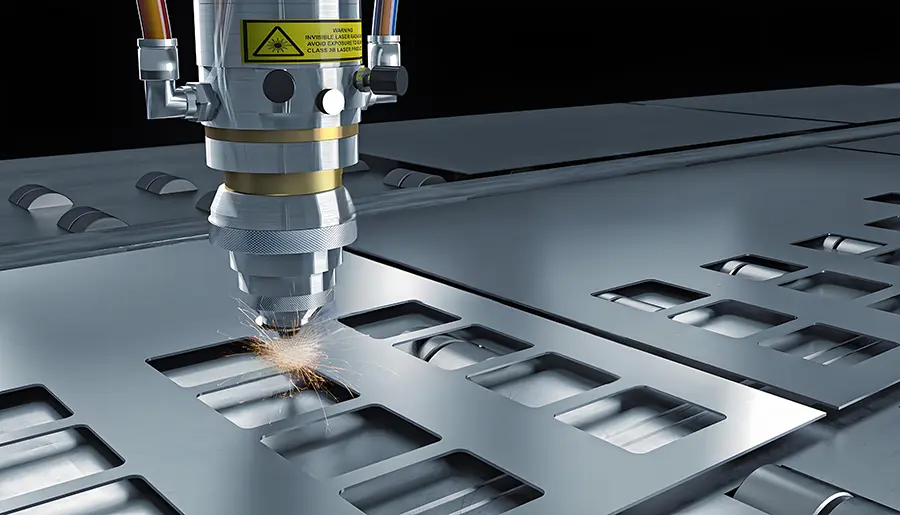
Mirrors and Optics
Mirrors at both ends of the laser tube form an optical resonator. One mirror is fully reflective, while the other is partially reflective, allowing a portion of the light to exit as the laser beam. Additional optics, such as lenses and beam expanders, shape and direct the beam for specific applications.
Power Supply
The power supply provides the necessary electrical energy to excite the gas mixture. It must deliver a stable and controlled current to ensure consistent laser performance.
Advantages of CO₂ Lasers
CO₂ lasers offer several benefits that make them suitable for a wide range of applications.
High Efficiency
CO₂ lasers have a relatively high electrical-to-optical efficiency, often around 10-20%, which is favorable compared to other laser types.
Versatility
They can process various materials, including metals, plastics, wood, glass, and textiles, making them ideal for diverse industrial tasks.
Precision and Quality
The coherent and focused beam allows for precise cutting and engraving, resulting in high-quality finishes with minimal material waste.(Baison)
Applications of CO₂ Lasers
The unique properties of CO₂ lasers have led to their adoption in multiple fields, each leveraging the laser's capabilities for specific purposes.
Industrial Applications
In the industrial sector, CO₂ lasers are integral to manufacturing processes that require precision and efficiency.
Cutting and Engraving
CO₂ lasers are widely used for cutting and engraving materials such as:
Metals: Steel, aluminum, and copper.
Plastics: Acrylic, polycarbonate, and PVC.
Wood: Plywood, MDF, and hardwoods.
Textiles: Fabrics and leather.
The laser's ability to produce clean cuts and intricate designs enhances product quality and reduces post-processing requirements.
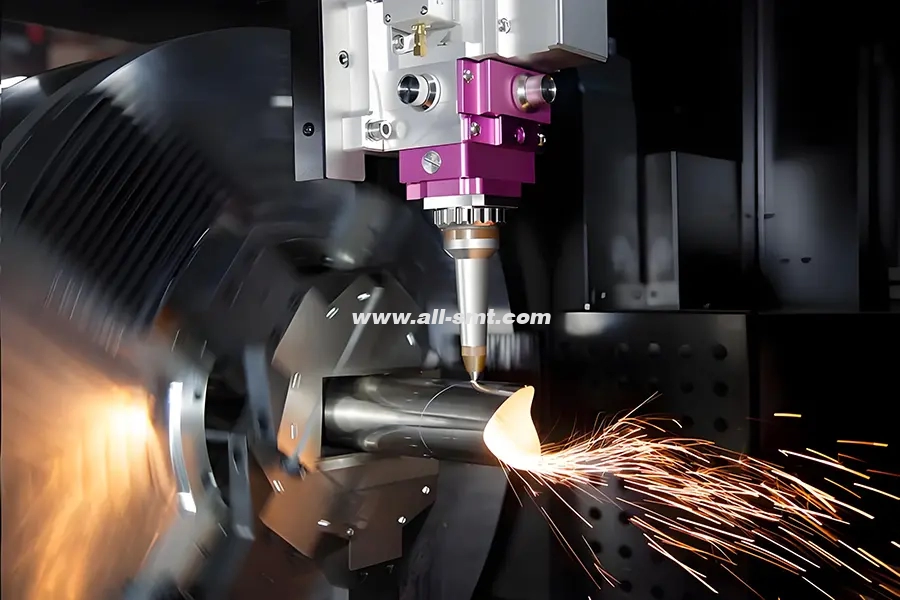

Marking and Etching
CO₂ lasers are employed to mark and etch serial numbers, barcodes, logos, and other identifiers on products. This non-contact method ensures durability and legibility without compromising the material's integrity.
Medical Applications
In medicine, CO₂ lasers have revolutionized surgical procedures by offering minimally invasive options with improved outcomes.
Dermatology
CO₂ lasers are used for skin resurfacing treatments to address:
Wrinkles and Fine Lines: Stimulating collagen production for smoother skin.
Scars: Reducing the appearance of acne and surgical scars.
Pigmentation Issues: Treating sunspots and melasma.
These procedures promote skin rejuvenation with shorter recovery times compared to traditional methods.
Surgical Procedures
CO₂ lasers are utilized in various surgical specialties, including:
Otolaryngology: Treating vocal cord lesions and nasal obstructions.
Gynecology: Performing cervical and vaginal surgeries.
Dentistry: Conducting soft tissue procedures with reduced bleeding and discomfort.
The laser's precision minimizes damage to surrounding tissues, leading to faster healing and fewer complications.
Scientific and Research Applications
CO₂ lasers play a vital role in scientific research due to their stable output and specific wavelength.
Spectroscopy
In spectroscopy, CO₂ lasers are used to analyze molecular compositions by measuring the absorption and emission of infrared light. This technique aids in environmental monitoring and chemical analysis.
Material Processing Research
Researchers utilize CO₂ lasers to study material behaviors under high-energy conditions, contributing to advancements in manufacturing technologies and material sciences.
Maintenance and Repair of CO₂ Lasers
Proper maintenance and timely repair of CO₂ lasers are crucial to ensure their longevity and optimal performance.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
CO₂ lasers may encounter various issues during operation.
Power Output Decline
A decrease in laser power can result from:
Gas Degradation: Over time, the gas mixture may deteriorate, reducing efficiency.
Mirror Contamination: Dust and debris on mirrors can obstruct the laser path.
Tube Wear: The laser tube's components may degrade with prolonged use.
Regular inspection and cleaning can mitigate these problems.
Beam Misalignment
Misalignment of optical components can lead to:
Inconsistent Cutting Quality: Uneven or incomplete cuts.
Increased Wear: Strain on mechanical parts due to improper beam focus.
Aligning mirrors and lenses ensures accurate beam delivery.
Preventive Maintenance Practices
Implementing routine maintenance schedules can prevent unexpected failures.
Regular Cleaning
Cleaning optical components, such as mirrors and lenses, prevents buildup that can hinder performance.
Cooling System Checks
Ensuring the cooling system functions correctly prevents overheating, which can damage the laser tube and other components.
Software Updates
Keeping control software up to date enhances functionality and security.
Professional Repair Services
When issues arise that exceed in-house capabilities, seeking professional repair services is advisable.
Diagnostic Assessments
Technicians can perform comprehensive diagnostics to identify underlying problems accurately.
Component Replacement
Professionals can replace worn or damaged parts with manufacturer-approved components, ensuring compatibility and performance.
System Calibration
Post-repair calibration aligns the system for optimal operation, restoring precision and efficiency.
CO2 lasers are a cornerstone of modern technology, offering unparalleled precision and versatility across various industries. Understanding their operation, applications, and maintenance requirements is essential for maximizing their benefits. Regular upkeep and professional servicing ensure that these powerful tools continue to perform at their best, driving innovation and efficiency in countless fields

