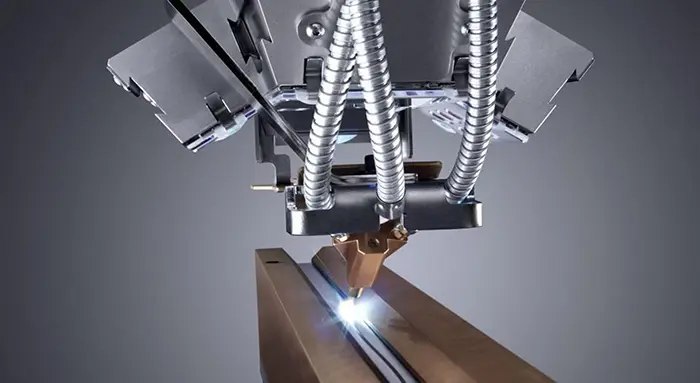
Laser engraving is a fascinating and highly efficient technology used in industries ranging from manufacturing and signage to jewelry design and custom gift creation. If you’ve ever wondered how a laser engraving machine works, this comprehensive guide will take you step-by-step through the entire process, from the basics of laser technology to the intricacies of engraving different materials.

What is Laser Engraving?
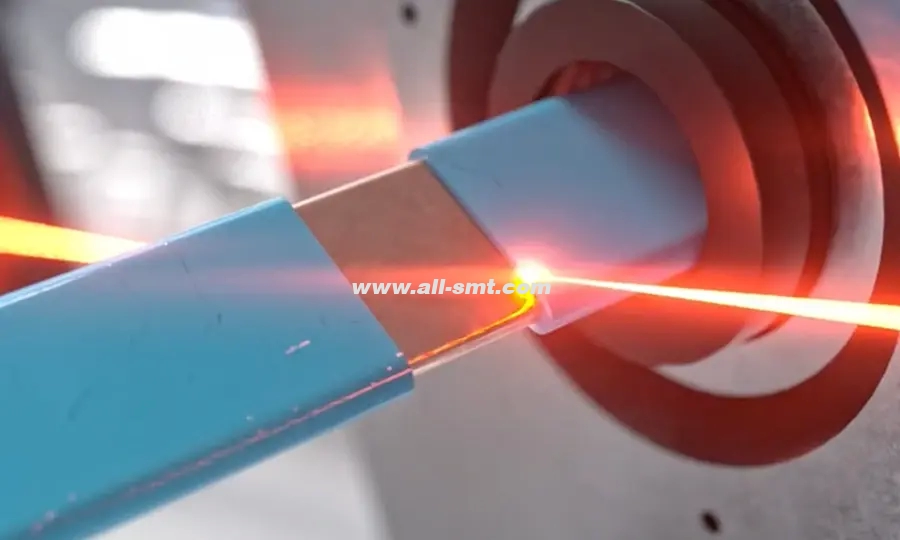
Laser engraving is the process of using a high-powered laser beam to remove material from the surface of an object. This results in a visible mark or pattern that can be permanent and highly detailed. Unlike printing or cutting, laser engraving physically alters the surface of the material by vaporizing or melting it away.
Key Components of a Laser Engraving Machine
Understanding the main parts of a laser engraving machine helps to understand how it functions. The key components include:
1. Laser Source
The laser source generates the beam that does the actual engraving. There are several types of lasers used:
CO2 lasers: Ideal for wood, acrylic, leather, glass, and more.
Fiber lasers: Best suited for metals and hard plastics.
Diode lasers: Commonly used for low-power applications.
2. Laser Tube or Module
This is where the laser beam originates. In CO2 systems, the laser tube is typically filled with gas (carbon dioxide) that is electrically stimulated to produce the laser beam.
3. Mirrors and Lenses
Mirrors direct the laser beam along the machine’s axis, while lenses focus the beam into a fine point for precision engraving.
4. Controller and Software
The controller interprets the digital design files and translates them into movements and laser pulses. Software allows users to upload designs and adjust settings like power, speed, and resolution.
5. Motion Control System
This includes motors and belts or rails that move the laser head (or the engraving bed) across the X and Y axes, and sometimes the Z-axis for depth control.
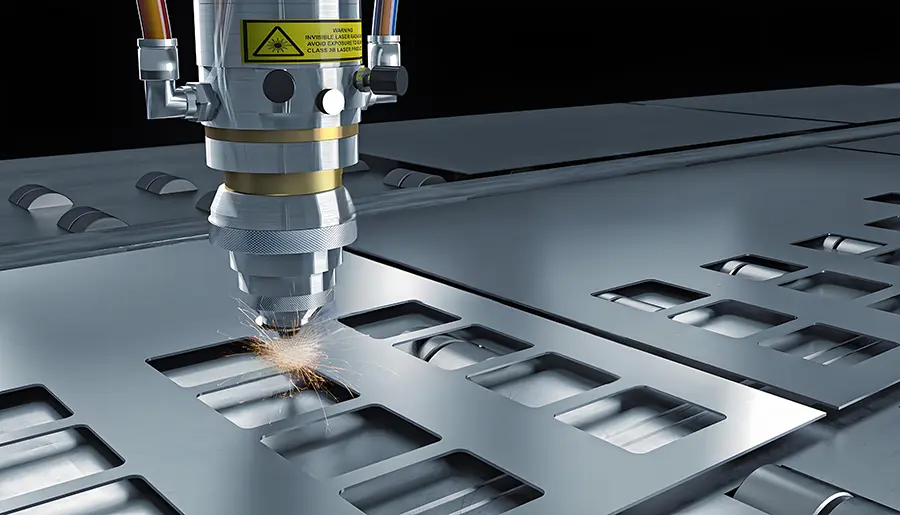
How Does Laser Engraving Actually Work?
Let’s break down the process into key steps:
Step 1: Design Preparation
A digital design is created using vector graphics software such as Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW, or CAD software. The design is then imported into the laser engraving software.
Step 2: Material Placement
The chosen material is placed securely on the engraving bed. The user must ensure that it is aligned properly to avoid errors during the process.
Step 3: Configuration and Calibration
Settings such as laser power, speed, frequency, and resolution are configured. These parameters depend on the material type and the desired depth or clarity of the engraving.
Step 4: Focusing the Laser
Focusing ensures the laser beam is sharp and accurate. An unfocused laser results in blurry or inconsistent engravings. Machines may use manual or automatic focus systems.
Step 5: Engraving Begins
The laser beam begins engraving by following the digital path from the design. The beam interacts with the surface, removing material through:
Vaporization: Material is instantly turned into gas.
Melting: Material melts and evaporates.
Ablation: Material is removed layer by layer.
Types of Laser Engraving Techniques
1. Raster Engraving
Similar to how a printer works, raster engraving scans line by line. It is commonly used for photos and detailed artwork.
2. Vector Engraving
Here, the laser follows paths defined by vector lines. It’s more precise and is typically used for outlining shapes or text.
3. 3D Laser Engraving
This advanced method adjusts the laser intensity to carve deeper at certain points, creating a three-dimensional effect on the surface.
Materials Compatible with Laser Engraving
Laser engraving machines can work with a wide variety of materials, depending on the laser type:
Organic Materials:
Wood
Leather
Paper
Fabric
Non-Metallic Materials:
Acrylic
Glass
Rubber
Stone
Metallic Materials:
Stainless steel
Aluminum
Brass
Copper
Each material requires specific settings for optimal results. For example, wood engraves well at low speed and medium power, while metal may require a fiber laser with high intensity.
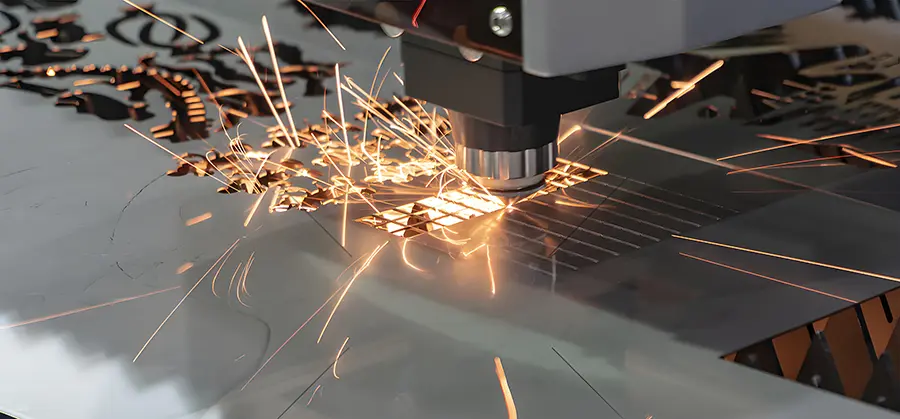
Safety Measures in Laser Engraving
Operating a laser engraving machine requires strict adherence to safety protocols:
1. Eye Protection
Lasers can cause permanent eye damage. Always use proper safety goggles that match the laser wavelength.
2. Ventilation
Laser engraving can release harmful fumes. Use a fume extractor or work in a well-ventilated area.
3. Material Safety
Never engrave unknown or PVC materials—they can release toxic chlorine gas.
4. Fire Hazards
Always monitor the machine while it’s operating. Laser beams can ignite flammable materials.
Benefits of Laser Engraving
Laser engraving is preferred over other marking techniques for several reasons:
Precision: Achieve intricate details with accuracy.
Durability: The marks are permanent and resistant to wear.
Non-contact Process: No physical force, reducing damage to delicate materials.
Versatility: Works on numerous materials and surfaces.
Speed: Fast turnaround for high-volume jobs.
Applications of Laser Engraving Machines
Laser engraving is used in multiple industries:
1. Manufacturing
Part labeling, serial numbers, and barcodes.
2. Jewelry
Personalized engraving on rings, pendants, and watches.
3. Woodworking
Decorative carving and branding on furniture and crafts.
4. Electronics
Engraving on PCBs, casings, and components.
5. Signage
Creating logos, signs, and nameplates.
6. Gifts and Customization
Photo engraving on glass, leather, and acrylic.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance ensures your laser engraving machine runs smoothly:
Clean lenses and mirrors regularly.
Check for alignment and recalibrate as needed.
Replace worn belts or motors.
Monitor software for updates.
Common issues:
Laser not firing: Could be a power supply or tube issue.
Inconsistent engraving: Often caused by focus or speed settings.
Smoke stains: Poor ventilation or engraving too slowly.
Future Trends in Laser Engraving
The future of laser engraving looks promising, with trends such as:
AI integration: Smarter design recognition and automated adjustments.
Compact desktop units: Affordable options for small businesses and hobbyists.
Green lasers: For more environmentally friendly operations.
Cloud-based control: Remote operation and file sharing.
Laser engraving machines have revolutionized how we mark and decorate materials. Understanding how they work—from laser generation to material interaction—can help you maximize their potential, whether you're a hobbyist, business owner, or technician. With proper use, maintenance, and safety practices, these machines offer endless possibilities for personalization, branding, and industrial use.
Whether you're looking to invest in a machine or simply learn more about the technology, we hope this guide has illuminated the working principles and practical applications of laser engraving machines.
Need help repairing or optimizing your laser engraving machine? Our experienced technicians are here to help. Contact us for expert support and fast service!