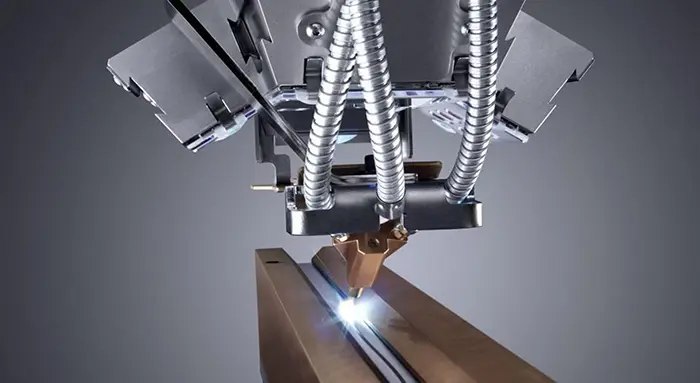
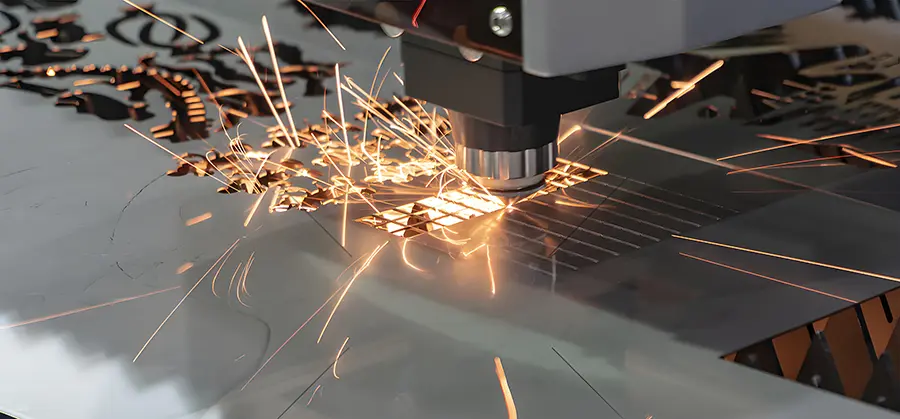
In the modern era of digital manufacturing and high-precision fabrication, CNC laser machines have revolutionized how we cut, engrave, and shape materials. But what exactly is a CNC laser? How does it work, and why is it so widely used across industries? This article will provide a comprehensive overview of CNC laser technology, its types, applications, advantages, and key considerations for businesses and hobbyists alike.
What Does CNC Laser Mean?
The term CNC laser combines two powerful technologies: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) and laser cutting or engraving. In essence, a CNC laser machine is a computer-controlled device that uses a highly focused beam of light to cut, engrave, or mark various materials with extreme precision.
CNC: A system where computer programs guide the movement of machine components based on a digital design.
Laser: An intense, focused beam of coherent light that can melt, burn, or vaporize material.
Together, these systems allow for automated, high-speed, high-accuracy material processing.
How Does a CNC Laser Work?
A CNC laser cutting machine follows a simple yet powerful principle. A digital design file—usually created in CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software—is loaded into the machine’s control system. Based on this file, the machine uses motors and controllers to move a laser head over the material. The laser beam is either pulsed or continuous, depending on the task.
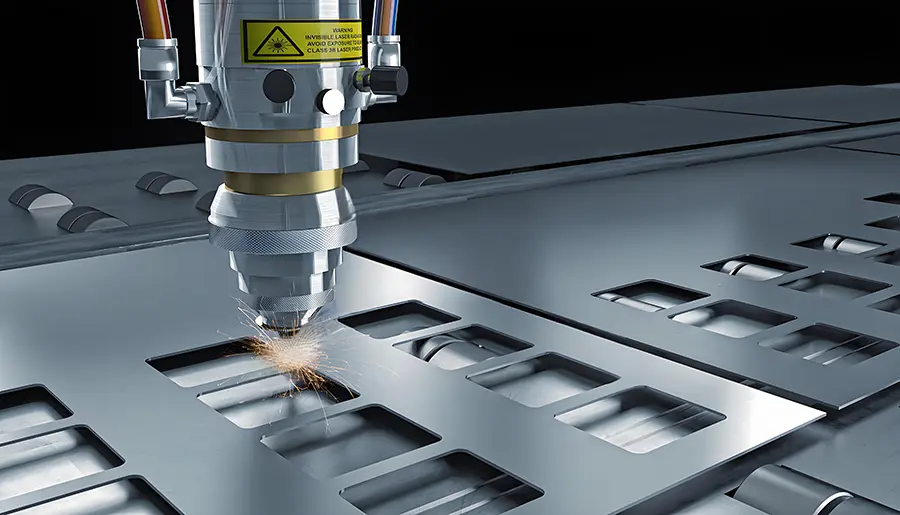
Step-by-Step Process:
Design Creation: The operator creates a design using CAD software.
File Conversion: The file is converted into a machine-readable format (like G-code).
Material Placement: The workpiece is placed on the machine bed.
Laser Calibration: Power, speed, and focus are adjusted for the material.
Execution: The laser follows the programmed path to cut or engrave the material.
This automated process ensures consistent quality, repeatability, and minimal material waste.
Types of CNC Laser Machines
There are several types of CNC laser machines, each suited for specific tasks and materials. The most common include:
1. CO2 Laser Machines
How it works: Uses carbon dioxide gas as the laser medium.
Wavelength: ~10.6 microns.
Best for: Wood, acrylic, leather, paper, plastic, glass.
Advantages: Affordable, good for non-metal materials.
2. Fiber Laser Machines
How it works: Uses a solid-state laser source amplified through optical fibers.
Wavelength: ~1.06 microns.
Best for: Metals (steel, aluminum, brass), some plastics.
Advantages: High power efficiency, long service life, low maintenance.
3. Nd:YAG Laser Machines
How it works: Uses a crystal (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet) as the medium.
Best for: Metals and some ceramics.
Advantages: High peak power for deep marking or engraving.
Each type offers unique benefits depending on the application. CO₂ lasers are ideal for soft materials, while fiber lasers dominate the metal fabrication industry.

Common Applications of CNC Laser Machines
CNC laser machines serve a wide range of industries and purposes. Here are the most common applications:
1. Laser Cutting
One of the most well-known uses, CNC laser cutting delivers clean edges with minimal thermal distortion. It’s used to cut:
Sheet metal
Acrylic panels
Wood planks
Plastic films
2. Laser Engraving
Engraving involves removing a surface layer to create text or patterns. Commonly engraved items include:
Awards and trophies
Barcodes and serial numbers
Decorative items
Industrial parts
3. Laser Marking
Unlike engraving, laser marking alters the surface without removing material. It’s used for:
Branding
QR codes
Component labeling
4. Prototyping and Product Development
CNC laser machines are essential tools in rapid prototyping, where quick turnaround and high precision are critical.
Benefits of CNC Laser Technology
Why are CNC lasers preferred over traditional cutting and engraving tools? The answer lies in their unmatched benefits.
1. Precision and Accuracy
CNC lasers can achieve tolerances of ±0.01 mm or better, making them ideal for intricate patterns and high-spec designs.
2. Speed and Efficiency
High-speed cutting reduces production times. Fiber lasers, in particular, can cut metal several times faster than traditional methods.
3. Minimal Material Waste
The narrow laser kerf (cut width) means less material is lost, which reduces costs and environmental impact.
4. Automation and Repeatability
Once a program is set, the machine can run 24/7 with identical results, reducing human error.
5. Versatility
One machine can work with multiple materials and switch between cutting and engraving modes easily.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite their advantages, CNC lasers are not perfect for every situation. Understanding the limitations helps in making an informed decision.
1. Initial Cost
CNC laser systems, especially high-power fiber lasers, can be expensive. However, they pay off in long-term productivity.
2. Material Limitations
Not all lasers can process all materials. For instance:
CO₂ lasers struggle with thick metals.
Fiber lasers are not ideal for transparent acrylics.
3. Maintenance
Optical systems and moving parts require regular cleaning and calibration to maintain accuracy.
4. Safety Concerns
Laser beams are powerful and potentially dangerous. Proper laser safety measures, including eyewear and shielding, are essential.
CNC Laser vs. CNC Router: What’s the Difference?
Both CNC lasers and CNC routers use computer control to manipulate materials, but they differ in methodology:
| Feature | CNC Laser | CNC Router |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Tool | Focused laser beam | Rotating mechanical bit |
| Precision | Very high | Moderate to high |
| Material Removal | Burns or vaporizes | Cuts or carves |
| Noise Level | Quiet | Noisy |
| Material Suitability | Great for thin or delicate materials | Better for thick or dense materials |
In general, laser machines are chosen for fine detail, while routers handle bulk material removal.
Choosing the Right CNC Laser Machine
When selecting a CNC laser, consider the following factors:
1. Material Type and Thickness
CO₂ for wood, acrylic, leather.
Fiber laser for steel, aluminum, and brass.
2. Cutting Area
Choose a bed size that accommodates your largest expected workpieces.
3. Laser Power
40–150W for CO₂.
500W–6000W+ for fiber lasers, depending on metal thickness.
4. Software Compatibility
Ensure the machine works with common file formats like DXF, SVG, AI, or PDF.
5. Budget
Factor in not only the purchase cost but also installation, training, and operational costs.
CNC Laser Maintenance Tips
Maintaining your CNC laser ensures long-term performance. Here are some key maintenance practices:
Clean the lens and mirrors regularly to avoid power loss.
Check and align the beam path if cutting performance drops.
Replace filters and coolant in machines with water-cooled systems.
Update firmware and software periodically.
Proper maintenance can extend your machine’s lifespan by years.
The Future of CNC Laser Technology
As manufacturing trends move toward automation, CNC laser machines will continue evolving. Future developments include:
AI-powered optimization for faster pathing.
Hybrid systems combining laser and mechanical tools.
Automated material loading for lights-out production.
Emerging technologies like ultrafast lasers and blue laser diodes also promise to broaden the material range and enhance performance.
Conclusion: Why CNC Lasers Matter
So, what is a CNC laser? It is a powerful tool that merges computer precision with laser technology to transform how materials are cut and engraved. Whether you’re in aerospace, signage, medical devices, or hobby-level crafting, CNC lasers offer:
High-speed operation
Unmatched precision
Design flexibility
Scalable production
With proper selection, setup, and maintenance, CNC lasers can significantly enhance productivity and open new creative possibilities for your projects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can a CNC laser cut metal?
Yes, particularly fiber lasers. They can cut various metals including steel, aluminum, brass, and copper.
Q2: What is the difference between laser cutting and laser engraving?
Laser cutting slices through the material completely. Laser engraving removes only the surface layer to create a design or text.
Q3: Are CNC lasers safe to use at home?
Some desktop CO₂ lasers are designed for hobbyists, but proper ventilation and eye protection are necessary.
Q4: How long does a CNC laser machine last?
With regular maintenance, a good-quality machine can last 8–15 years or more.