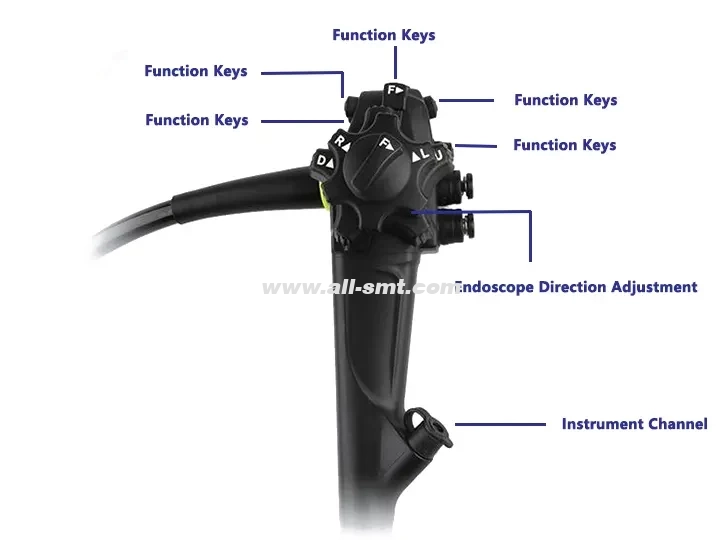
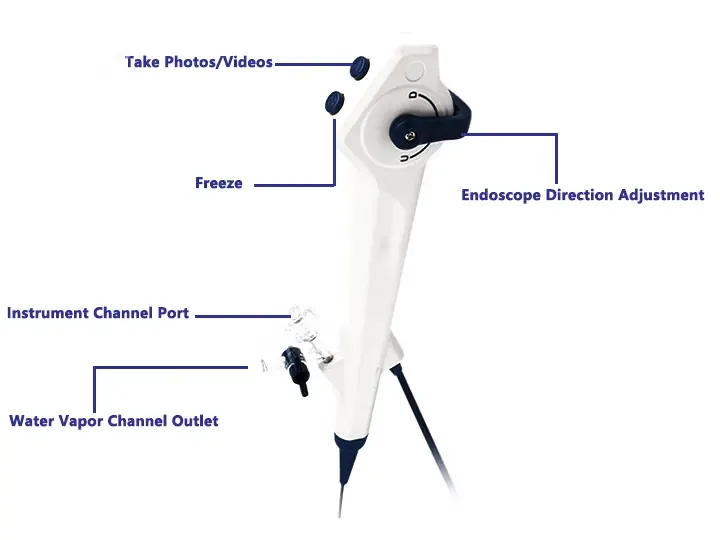
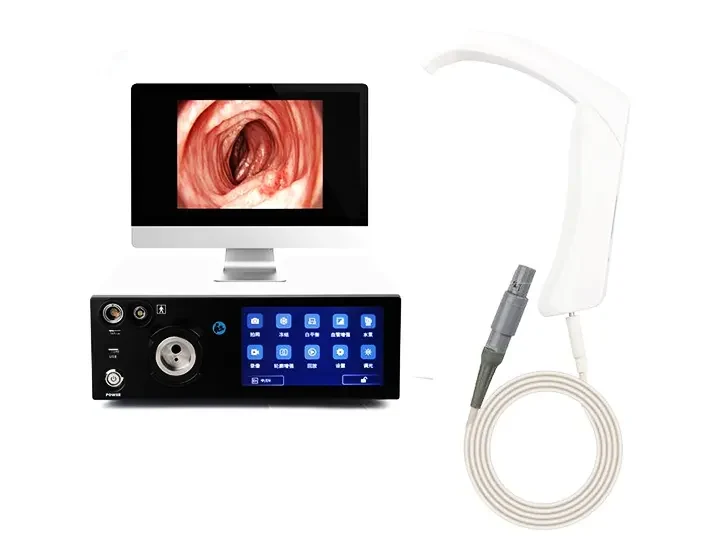
The body of a medical endoscope is the core component of the device, which directly determines the imaging quality and operating performance. According to the structure, purpose and material of the body, it is mainly divided into the following categories:
1. Rigid Endoscope
Features:
Inflexible: It is composed of a metal barrel and an optical lens, and the body is rigid
High resolution: The optical lens transmits images without pixel loss (such as 4K/8K imaging)
High durability: It can be sterilized at high temperature and high pressure, and its service life is up to 5-10 years
Typical applications:
Laparoscope: used for minimally invasive surgery (such as cholecystectomy)
Arthroscopy: knee and shoulder joint examination and surgery
Sinusoscope: ENT surgery
Representative brands:
Karl Storz (Germany): TIPCAM 3D stereo laparoscope
Olympus: VISERA 4K ultra-high definition system
2. Flexible Video Endoscope Endoscope
Features:
Bendable: The front end is controlled by an electric motor (≥180° up, down, left, and right)
Electronic imaging: The front end integrates a CMOS/CCD sensor, and the image is transmitted via a cable
Multi-function channel: Biopsy forceps, electrosurgical knife and other instruments can be inserted
Typical applications:
Gastroenteroscope: gastroscopy, colonoscopy (such as Olympus GIF-H290)
Bronchoscopy: lung diagnosis and treatment (such as Fuji EB-580S)
Choledochoscopic: ERCP surgery (such as Pentax ED-3490TK)
Technical highlights:
Ultra-thin diameter design: The minimum diameter is only 2.8mm (such as transnasal gastroscope)
Electronic staining: NBI/BLI enhances lesion contrast
3. Fiberoptic endoscope Endoscope
Features:
Fiber optic transmission: images are transmitted through tens of thousands of glass optical fibers
Low cost: significantly more expensive than electronic endoscopes
Images are in a grid pattern: resolution is lower than electronic endoscopes
Application scenarios:
Primary hospitals: alternatives when budgets are limited
Special environments: such as high temperatures/electromagnetic interference scenarios (fiber optic anti-interference)
Representative products:
Olympus: fiber bronchoscope BF-P60
Domestic: some nasopharyngeal examination mirrors
4. Capsule Endoscope
Features:
Non-invasive examination: patients swallow capsules and take images as the digestive tract moves
Wireless transmission: battery life of 8-12 hours, images are transmitted to an external recorder
Disposable use: avoid cross infection
Application areas:
Small intestine examination: difficult to reach with traditional endoscopes (such as Given Imaging's PillCam)
Children/patients with poor tolerance: no anesthesia required
5. Special function endoscopes
(1) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
Ultrasound probe integrated in the endoscope: evaluates the digestive tract wall and surrounding organs (such as the pancreas)
Representative model: Olympus EU-ME2
(2) Fluorescence endoscope
ICG/NIR fluorescence navigation: real-time display of tumors or blood flow (such as Storz IMAGE1 S)
(3) Confocal laser endoscope (pCLE)
Cellular imaging: used for early diagnosis of cancer (such as Mauna Kea's Cellvizio)
Core parameter comparison of endoscope
Type Resolution Bendable Sterilization method Lifespan
Hard endoscope Optical 4K/8K No High temperature and high pressure 5-10 years
Electronic soft endoscope 1080p/4K Yes Immersion/low temperature sterilization 3-5 years
Fiber endoscope Standard definition Yes Immersion 2-3 years
Capsule endoscope 480p-1080p - Disposable Single
Future development trends
Smaller and smarter: diameter below 3mm + AI real-time diagnosis
Modular design: quick replacement of lenses/sensors
Disposable electronic endoscope: balance cost and infection control (such as Ambu aScope)
Summary
The choice of endoscope body needs to balance imaging quality, flexibility, durability and cost. Hard endoscopes are suitable for precision surgery, electronic soft endoscopes dominate the diagnosis field, and new technologies such as capsule endoscopes are expanding non-invasive inspection scenarios. In the future, intelligence and miniaturization will be the main development direction.