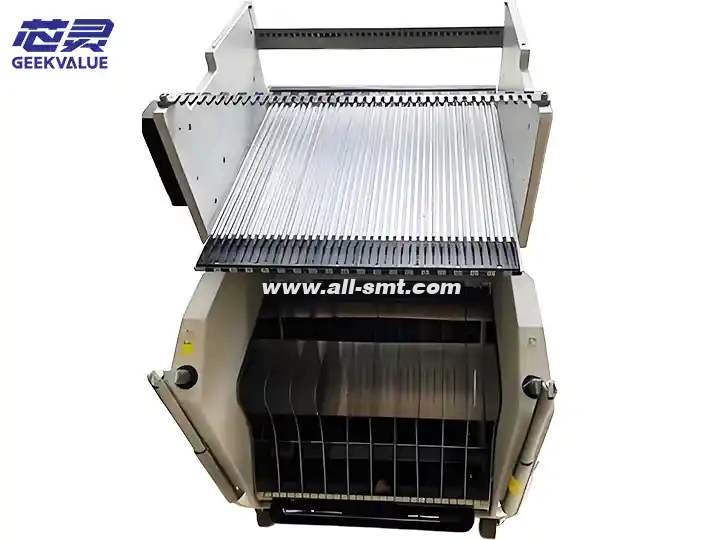
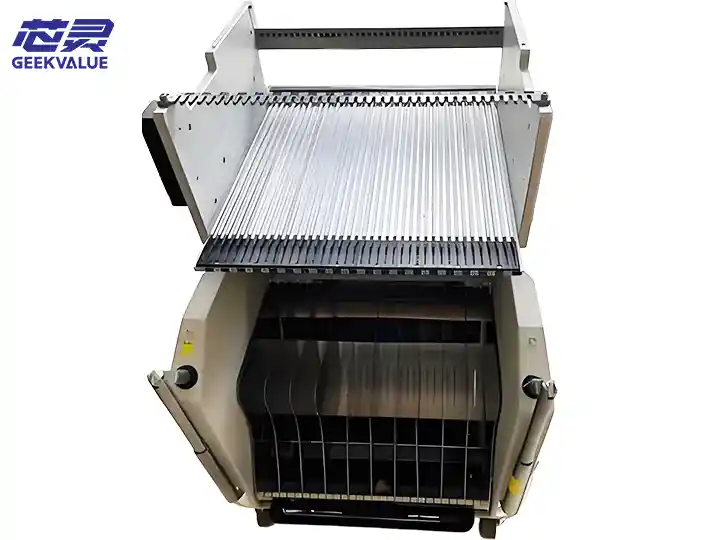
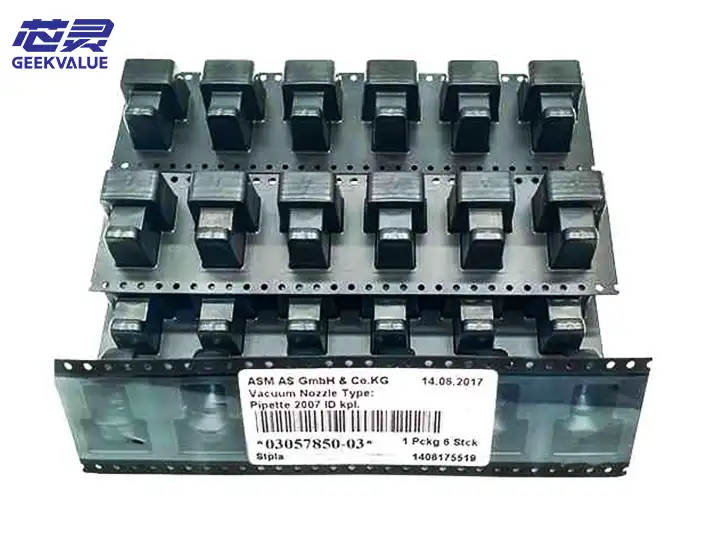
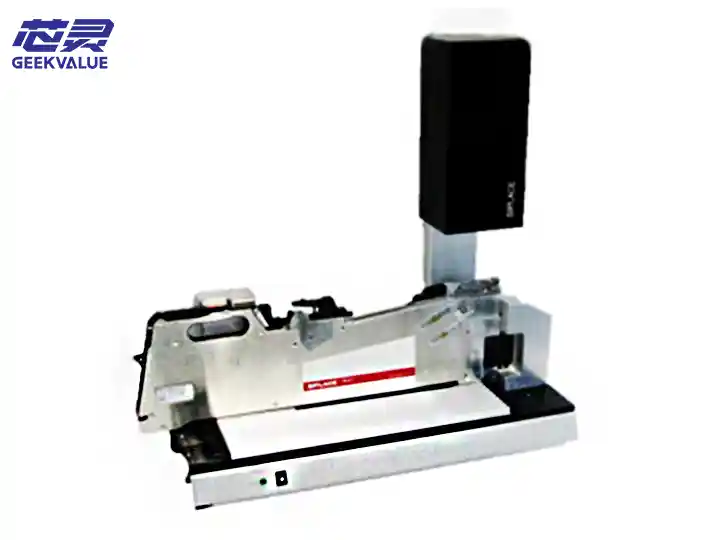
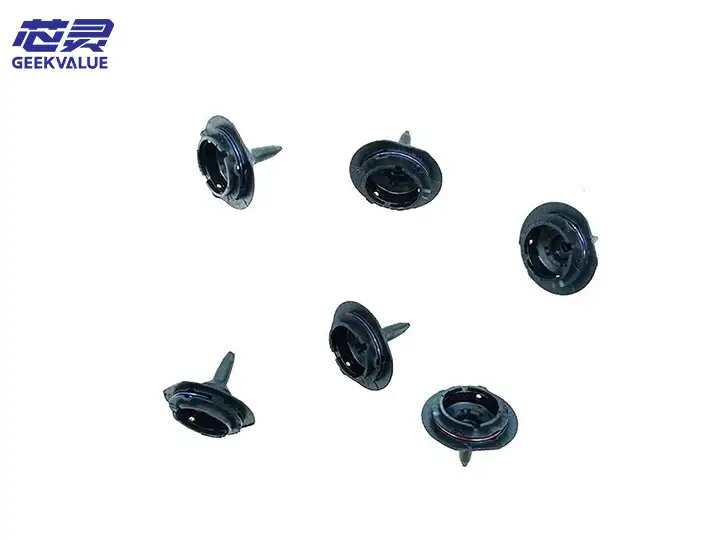
The ASM 40-Slot Feeder Trolley is an intelligent feeding system designed for SIPLACE/ASM placement machines. It can simultaneously load 40 SMT feeders of various specifications such as 8mm/12mm/16mm/24mm/32mm/44mm to achieve efficient and automated feeding. It is usually used in conjunction with ASM X series (such as X4i, X2S) and S series placement machines, and is a core component of medium and large SMT production lines.
2. Core functions and roles
(1) Main functions
Multi-station feeding: supports 40 feeders working simultaneously to reduce downtime for material change.
Fast line change: The entire feeder trolley can be pre-loaded with the next batch of materials to achieve hot swap.
Intelligent identification: Some models support RFID or barcode scanning to automatically identify material information.
Strong compatibility: Applicable to ASM's full range of electric/pneumatic feeders (such as 0401, 0808, etc.).
(2) Core role
Improve production efficiency: Reduce manual material change time and support continuous production.
Reduce error rate: Avoid feeding errors through standardized feeding management.
Flexible adaptation: Applicable to multi-variety, small batch (NPI) and large batch production modes.
3. Technical Specifications
Parameters Specifications
Number of feed stations 40 (8mm/12mm/16mm/24mm/32mm/44mm feeders can be mixed)
Dimensions (length × width × height) Approximately 1200mm × 600mm × 1000mm (specific models may vary slightly)
Weight No-load approximately 50-70kg (up to 100kg or more when fully loaded with feeders)
Power supply Some models support electric drive (24V DC), ordinary models are manual push-pull type
Positioning accuracy ±0.1mm (to ensure accurate docking between the feeder and the placement machine)
Applicable models SIPLACE X4i, X2S, SX series, TX series, etc.
Communication interface High-end models support Profinet/Ethernet communication and are linked to the MES system
4. Structural composition
(1) Mechanical structure
Frame body: high-strength aluminum alloy/steel frame with anti-vibration casters (some with brake function).
Station rails: Precision rail design ensures smooth insertion and removal of feeders.
Positioning pins/clip: Used to fix the feeder to prevent vibration and deviation.
(2) Electrical system (electric model)
Servo drive motor: Controls the automatic docking of the material cart and the placement machine.
RFID/barcode scanning module: Automatically identifies the feeder information.
Sensor system: Detects whether the feeder is installed in place.
(3) Auxiliary functions
LED status indicator: Displays the use status of the material station (such as empty, working, and lack of material alarm).
Anti-static design: Prevents materials from being contaminated or damaged by static electricity.
5. Usage process
Pre-loading: Install the feeder on the material cart in an offline state, and bind the material information through the MES system or barcode scanning.
Docking the placement machine: Push the material cart to the placement machine interface and lock the position automatically or manually.
System identification: The placement machine reads the feeder data and verifies whether the material is correct.
Start production: The SMT machine takes materials from the material cart and mounts them according to the program.
Line change operation: After production is completed, the entire material cart can be quickly replaced with the next batch of material carts.
6. Precautions for use
(1) Installation and commissioning
Horizontal calibration: The material cart must be placed on a flat surface to avoid poor docking of the feeder due to tilting.
Feeder installation direction: Make sure that all feeders are inserted in the same direction (labels facing outward).
Locking check: After pushing the SMT machine into place, make sure that the mechanical lock is in place to prevent it from being disengaged during production.
(2) Daily maintenance
Clean the guide rail regularly: Wipe it with a dust-free cloth to prevent dust accumulation from affecting the sliding of the feeder.
Check the sensor: Make sure that the RFID reader and photoelectric sensor are working properly.
Lubricate mechanical parts: Add a small amount of grease (such as Shell Gadus S2) to the guide rail and roller every 3 months.
(3) Safe operation
No overloading: Avoid stacking heavy objects or non-standard feeders one the material cart.
Slow down when moving: When moving an electric material truck in a workshop, be careful to avoid people and equipment.
Emergency stop: For electric models, be familiar with the location of the emergency stop button.
7. Common faults and solutions
Fault phenomenon Possible cause Solution
Feeder cannot be identified 1. RFID tag is damaged
2. Sensor is contaminated 1. Replace the tag
2. Clean the sensor
Cart docking is offset 1. Positioning pin is worn
2. Uneven ground 1. Replace the positioning pin
2. Adjust the position of the trolley
Electric trolley cannot move 1. Low battery
2. Motor failure 1. Charging
2. Contact after-sales maintenance
Feeder does not eject smoothly 1. Guide rail is deformed
2. Feeder buckle is too tight 1. Correct the guide rail
2. Adjust the buckle tension
8. Upgrade and optimization suggestions
Install RFID system: realize the whole process traceability of materials and reduce manual input errors.
Upgrade electric drive: change the manual trolley to automatic docking model to improve line change efficiency.
Integrate MES system: upload material consumption data in real time through Profinet interface.
9. Summary
The ASM 40 station material car is the core auxiliary equipment for efficient SMT production. Its modular design, fast material change capability and intelligent recognition function can significantly improve the utilization rate of the placement machine. Correct installation, regular maintenance and standardized operation are the key to ensure its long-term stable operation. For mass production scenarios, it is recommended to choose an electric model to further optimize production efficiency.